
Design Patterns
- Posted by Yomna Anwar
- On August 23, 2022
What are design patterns?
Design patterns are general solutions providing a way to solve problems that commonly arise during software development. These solutions are proven through tests, trial and errors to be effective in improving overall code efficiency and readability. A design pattern is a template or a general concept that a developer can apply while developing a software, it is not a solution that can be transformed directly into code.
Why use design patterns?
Using design patterns to aid with development can help improve code quality, accelerate the process, and prevents the need to create a new pattern every time a design problem arises.
Types of design patterns
According to a book titled ‘Design Patterns – Elements of Reusable Object-Oriented Software’ published in 1994 by four authors (Known as Gang of Four) there are 23 different design patterns. These design patterns can mainly be classified into three categories:
- Creational Design Patterns
- Structural Design Patterns
- Behavioral Design Patterns
Each category is different in terms of complexity, level of detail and the scale of system being designed.
Creational Design Patterns
Creational Design Patterns tackles how to handle the creation of new objects. These patterns increase flexibility and reusability of code.
Examples of creational design patterns include:
- Factory Method Pattern
- Singleton Pattern
- Prototype Pattern
Structural Design Patterns
Structural Design Patterns focuses on how objects connect and relate with one another. These patterns help create structures using multiple objects and classes.
Examples of structural design patterns include:
- Facade Pattern
- Adapter Pattern
- Composite Pattern
- Proxy Pattern
- Decorator Pattern
Behavioral Design Patterns
Behavioral Design Patterns addresses how each object has a different purpose and work towards a common goal. These patterns focus mainly on the communication between objects and responsibility distribution between one object and the other.
Examples of behavioral design patterns include:
- Template Method Pattern
- Chain of Responsibility Pattern
- Command Pattern
- Observer Pattern
- Strategy Pattern
Differences between similar design patterns
Strategy Pattern Vs Factory Method Pattern
Strategy Pattern
The Strategy design pattern is a type of behavioral design patterns that is used when representing multiple objects each having a different strategy of performing a behavior. In this pattern there is a context object that preforms that behavior based on desired strategy.
UML Diagram
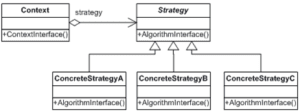
Figure 1 Khosravi, Khashayar & Guéhéneuc, Yann-Gaël. (2022). A Quality Model for Design Patterns.
When to use Strategy Pattern?
This pattern can be used when needed to switch between different variations of algorithms performing a certain behavior on runtime.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Easily alternate between different strategies on runtime | Clients must know the different strategies and when to use the appropriate one |
| Makes code cleaner by separating different functional logic into different classes (each class has a different strategy) | Increased number of objects in an application |
Example:
// ParkingStratetgy.java
public interface ParkingStratetgy {
public int parkCar(int carLicenseNumber);
}
// ParrallelPark.java
public class ParrallelPark implements ParkingStratetgy {
@Override
public String parkCar (int carLicenseNumber) {
return “Car with license plate: “+carLicenseNumber+” parked parallelly”;
}
}
// PerpendicularPark.java
public class PerpendicularPark implements ParkingStratetgy {
@Override
public String parkCar (int carLicenseNumber) {
return “Car with license plate: “+carLicenseNumber+” parked perpendicularly”;
}
}
// ParkingSpace.java
public class ParkingSpace {
private ParkingStratetgy parkingStratetgy;
public parkCar (ParkingStratetgy parkingStratetgy){
this. parkingStratetgy = parkingStratetgy;
}
public String parkCar(int carLicenseNumber){
return parkingStratetgy. parkCar(carLicenseNumber);
}
}
//StrategyPatternDemo.java
public class StrategyPatternDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ParkingSpace parkingSpace = new ParkingSpace(new PerpendicularPark ());
System.out.println(parkingSpace. parkCar (123));
parkingSpace = new ParkingSpace (new ParrallelPark ());
System.out.println(parkingSpace. parkCar (756));
}
}
//Output
// Car with license plate: 123 parked perpendicularly
// Car with license plate: 756 parked parallelly
Factory Method Pattern
The Factory Method design pattern is a type of creational design patterns that is used to create an object by defining an interface that lets subclasses decide on the object type being created. This pattern abstracts creation logic from the clients.
UML Diagram
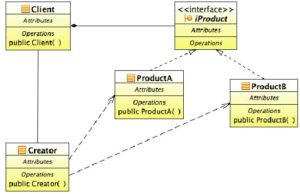
Figure 2 Fojtik, Rostislav. (2014). Design Patterns in the Teaching of Programming. Procedia – Social and Behavioral Sciences. 143. 10.1016/j.sbspro.2014.07.493.
When to use Factory Method Pattern?
This pattern can be used when wanting a class to differ instantiation to its subclasses rather than the class itself.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Provides loose coupling | Increased number of integrated classes |
| Easier addition of new classes | In some cases, clients must subclass the creator class to create a concrete product object. |
Example:
//Notification.java
public interface Notification {
void notifyUser();
}
//SMSNotification.java
public class SMSNotification implements Notification {
@Override
public void notifyUser()
{
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("Sending an SMS notification");
}
}
//EmailNotification.java
public class EmailNotification implements Notification {
@Override
public void notifyUser()
{
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("Sending an e-mail notification");
}
}
//PushNotification.java
public class PushNotification implements Notification {
@Override
public void notifyUser()
{
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("Sending a push notification");
}
}
//NotificationFactory.java
public class NotificationFactory {
public Notification createNotification(String channel)
{
if (channel == null || channel.isEmpty())
return null;
switch (channel) {
case "SMS":
return new SMSNotification();
case "EMAIL":
return new EmailNotification();
case "PUSH":
return new PushNotification();
default:
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unknown channel "+channel);
}
}
}
//NotificationService.java
public class NotificationService {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
NotificationFactory notificationFactory = new NotificationFactory();
Notification notification = notificationFactory.createNotification("SMS");
notification.notifyUser();
}
}
Similarities between Strategy Pattern and Factory Method Pattern
Both patterns have a main class that lets subclasses or implementation classes determine the way this main class works. In the case of Factory method pattern subclasses hold the creational logic of the main class. While in Strategy pattern, classes that implement the main class determine the behavior of certain functionalities of the main class.
Differences between Strategy Pattern and Factory Method Pattern
| Strategy Pattern | Factory Method Pattern |
| Behavioral pattern, used to implement certain operations in different ways depending on the object type | Creational pattern, used to create objects of different types |
| Based on delegation | Based on Inheritance |
Composite Pattern Vs Decorator Pattern
Composite Pattern
The Composite design pattern is composing objects into tree structures, allowing clients to interact with separate objects and compositions of objects in a similar matter.
UML Diagram
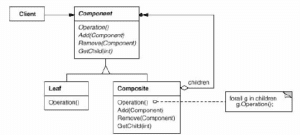
Figure 3 Chirila, Ciprian-Bogdan & Crescenzo, Pierre & Lahire, Philippe. (2005). Towards Reengineering: An Approach Based on Reverse Inheritance. Application to Java.
When to use Composite Pattern?
This pattern can be used when needed to treat a group of objects the same way as a single object.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Can be expanded easily | Challenging implementation of component interfaces |
| Accurately represents heavily nested object structures | Adjustment of composite properties is complicated |
Example:
//Department.java
public interface Department {
void printDepartmentName();
}
//FinancialDepartment.java
public class FinancialDepartment implements Department {
private Integer id;
private String name;
public void printDepartmentName() {
System.out.println(getClass().getSimpleName());
}
}
//SalesDepartment.java
public class SalesDepartment implements Department {
private Integer id;
private String name;
public void printDepartmentName() {
System.out.println(getClass().getSimpleName());
}
}
//HeadDepartment.java
public class HeadDepartment implements Department {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private List childDepartments;
public HeadDepartment(Integer id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.childDepartments = new ArrayList<>();
}
public void printDepartmentName() {
childDepartments.forEach(Department::printDepartmentName);
}
public void addDepartment(Department department) {
childDepartments.add(department);
}
public void removeDepartment(Department department) {
childDepartments.remove(department);
}
}
Decorator Pattern
The Decorator design pattern is wrapping a class with another class that provides additional functionalities without altering the original class methods signatures.
UML Diagram
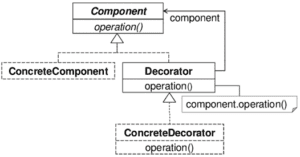
Figure 4 Kniesel, Günter & Binun, Alexander & Chatzigeorgiou, Alexander & Guéhéneuc, Yann-Gaël & Tsantalis, Nikolaos. (2009). DPDX – A Common Exchange Format for Design Pattern Detection Tools.
When to use Decorator Pattern?
This pattern is mainly used to alter project code to add functionalities without changing the existing core classes. It can also be used when wanting to reduce the number of classes needed to offer a combination of behaviors.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Functionalities are resource optimized | Challenging debugging process |
| Readable program code | Uses high number of objects |
Example:
//VisitEngine.java
public interface VisitEngine {
String getEngineeringOfficeId();
String getEngineeringOfficeCityId();
int getRemainingCapacity();
List calculateVisits();
}
//GroupOneDecorator.java
public class GroupOneDecorator implements VisitEngine {
private VisitEngine engine;
private int groupCapacity;
private Queue groupOneLicenses;
private int remainingCapacity;
private List generatedVisits;
public GroupOneDecorator(VisitEngine engine, int groupCapacity,
Queue groupOneLicenses) {
this.engine = engine;
this.groupCapacity = groupCapacity;
this.groupOneLicenses = groupOneLicenses;
generatedVisits = new ArrayList<>();
}
@Override
public List calculateVisits() {
List calculatedVisits = this.engine.calculateVisits();
generatedVisits.addAll(calculatedVisits);
remainingCapacity += groupCapacity;
return generatedVisits;
}
@Override
public String getEngineeringOfficeId() {
return engine.getEngineeringOfficeId();
}
@Override
public String getEngineeringOfficeCityId() {
return engine.getEngineeringOfficeCityId();
}
@Override
public int getRemainingCapacity() {
return remainingCapacity;
}
public int getGroupCapacity() {
return this.groupCapacity;
}
}
//GroupTwoDecorator.java
public class GroupTwoDecorator implements VisitEngine {
private VisitEngine engine;
private int groupCapacity;
private Queue groupTwoLicenses;
private int remainingCapacity;
private List generatedVisits;
public GroupTwoDecorator(VisitEngine engine, int groupCapacity, Queue groupTwoLicenses) {
this.engine = engine;
this.groupCapacity = groupCapacity;
this.groupTwoLicenses = groupTwoLicenses;
this.generatedVisits = new ArrayList<>();
}
@Override
public List calculateVisits() {
List calculatedVisits = this.engine.calculateVisits();
this.groupCapacity += engine.getRemainingCapacity();
generatedVisits.addAll(calculatedVisits);
remainingCapacity = groupCapacity;
return generatedVisits;
}
@Override
public String getEngineeringOfficeId() {
return engine.getEngineeringOfficeId();
}
@Override
public String getEngineeringOfficeCityId() {
return engine.getEngineeringOfficeCityId();
}
@Override
public int getRemainingCapacity() {
return remainingCapacity;
}
}
Similarities between Decorator Pattern and Composite Pattern
Both patterns aim to embed objects within another. The composite pattern embeds classes in a tree like structure while decorator pattern a class embeds another by wrapping to provide extra functionalities.
Differences between Decorator Pattern and Composite Pattern
| Composite Pattern | Decorator Pattern |
| Combine and represent multiple objects as one. (Can have a one-to-many relationship). | Enhances a single object. (Is a one-to-one relationship). |
| Focuses on aggregation and representation of objects. | Designed to add functionalities and embellish an object. |




