
Software Defined Network
- Posted by Sara Maged
- On August 22, 2023
What is SDN ?
Software defined networking (SDN) is a network management architecture approach in which the control and data planes are separated, allowing the network to be intelligently and centrally controlled, or programmed. by using a set of techniques to control, manage, and change the way networks are built and managed.
What does “programmed” mean, and why is it needed?
OpenFlow defined a programmable network protocol such that it could help manage and direct traffic among routers and switches, no matter which vendor made the underlying router or switch.
The need for SDN comes from how complex the networks have grown. SDN provides a single pane of glass (for configuration, management, and monitoring of network devices).
- Reducing deployment time
- Rapid and scalable deployment of network services
- Normalize interface with equipment and services
The idea of programmability is the basis for the most precise definition of what SDN is: a technology that separates the control plane management of network devices from the underlying data plane that forwards network traffic.
Types of SDN
- Open SDN
- The controller communicates with the switches using a sound-bound API with the help of the OpenFlow protocol.
- SDN via API
- The functions of remote devices like switches are invoked using conventional methods.
- The devices are provided with control points, enabling the controller to manipulate the remote devices using APIs.
- SDN via a hypervisor-based overlay network
- Hypervisor-based overlay networks are created over the physical network.
- The hypervisor controls the network traffic of the physical device by sending and receiving traffic to the virtualized networks. As a result, the edge devices control the virtual network.
How does SDN differ from Traditional Network ?
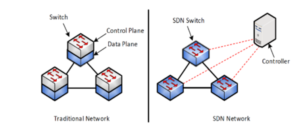
A traditional network is hardware-based, and it operates by making connections and running the network through switches, routers, and other physical infrastructure.
Traditional network plans are as follows:
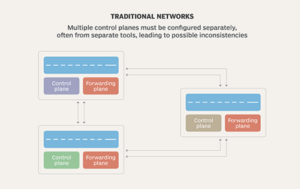
- The forwarding plane is responsible for the forwarding of data through a network device.
- The control plane is responsible for controlling the forwarding tables that the data plane uses.
- The management plane is integrated into the control plane; it is where we configure and monitor the network device.
- The data plane acts on the forwarding decisions, while the control and management planes learn and compute the forwarding decisions.
The physical placement of the control plane makes it more complex for an administrator to handle control plane traffic flow.
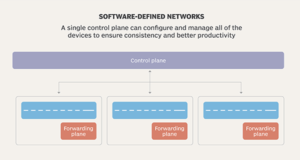
SDN on the other side is software-based, making it more flexible and providing administrators with the freedom to control the network, alter the configuration settings, and increase the network capacity without the need to add hardware since the control plane becomes software-based. We’ll dive into the SDN architecture next, but first let me display some of the benefits of SDN.
- Standard interface for centralized configuration, management, control, and monitoring of network devices: physical, virtual, and cloud.
- Simplify the process of provisioning new services. Admin deploys the policy while the controller figures out what needs to be provisioned.
- Allows the network to be managed as a whole and increases the ability to configure the network in a more predictable way.
- Rapid deployment of network services and infrastructure in a faster, more efficient manner.
SDN Architecture
A typical representation of SDN architecture separates the network into three distinct layers, connected through northbound and southbound APIs.
The northbound API is responsible for the communication between the highest application layer and the controller at the middle control layer.
The southbound API is responsible for the communication between the controller at the middle control layer and the lower networking elements at the data layer.
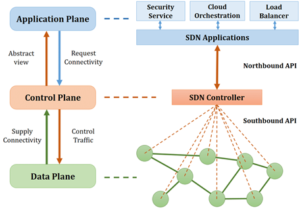
1- Application Layer
-
- Contains the SDN applications, which communicate network requirements to the controller
2- Control Layer
- Represents the centrally located SDN controller software that acts as the brain of the software-defined network.
- This controller contains SDN controllers, which provide centralized control of the devices in the data plane.
- The control layer is a critical point in the SDN; therefore, it would be considered a single point of failure.
3- Infrastructure Layer
- Contains network elements—a physical, virtual device that deals with traffic.
- This layer would be the physical one over which network virtualization would be laid down through the control layer.
These three layers communicate using respective northbound and southbound application programming interfaces (APIs).
API is a protocol that allows software to communicate with other software. Requests are sent to the network device, which responds.
Is SDN Secure?
SDN network security needs to be everywhere within a software-defined network (SDN). SDN security needs to be built into the architecture as well as delivered as a service to protect the availability, integrity, and privacy of all connected resources and information.
Several functions should be built within the SDN architecture to maintain its security, such as:
1- Securing the controller
- As the central decision point, access to the SDN controller needs to be tightly controlled.
2- Protecting the controller
- If the SDN Controller goes down, so does the network, which means the availability of the SDN Controller needs to be maintained.
3-Establishing Trust
- It is critical to safeguard communications throughout the network. This means ensuring the SDN Controller, the applications loaded on it, and the devices it manages are all trusted entities that are operating as they should.
4-Creating a Robust Policy Framework
- What’s needed is a system of checks and balances to make sure the SDN controllers are doing what you actually want them to do.
5-Conducting Forensics and Remediation
- When an incident happens, you must be able to determine what it was, recover, potentially report on it, and then protect against it in the future.
Security should not be limited to the architecture; how SDN security is deployed, managed, and controlled in an SDN environment is still up for debate in the following ways:
- Simple: to deploy, manage, and maintain in the highly dynamic SDN environment.
- cost-effective: to ensure security can be deployed everywhere,
- Secure: To protect against the latest advanced, targeted threats facing your organization.
What Does SDN Future Look Like?
- Software-defined networks have a bright future ahead since the storage and computing needs are ever-changing, and they don’t mesh well with the traditional hardware-based networks in data centers, large enterprises, or campus environments. In light of those events, SDN implements a precise alternative where various characteristics call for a dynamic and flexible approach. These situations have given SDN more importance and wider acceptance.
- Every network has frequently varying usage patterns and diverse traffic patterns. Therefore, they demand dynamic and adaptable traffic management and the capacity to achieve the required bandwidth.
- The prevalence of BYOD is growing as employees increasingly use their own high-end devices. Therefore, this challenges the networks to be flexible enough to support whatever devices users carry with them. These networks should also be highly secure to protect data and information, as well as to satisfy compliance regulations and standards.
- The increase in cloud services implies that users demand unrestrained access to applications, infrastructure, and IT resources, anywhere and anytime.




